Development Installation Procedures (Outdated)
The UF BRAVO Platform consist of 2 main components: Python Server and React Frontend. These two components can communicate through both Websocket and REST APIs, supported by Django Channels and Django REST Framework.
The documentation will walk through installation of both components; however, users may choose to use only one components without the other based on their need and customization. A common example would be to use Python Server ONLY to process and organize session files but without a web interface. The users then can perform custom analysis pipeline using Python, MATLAB, or R on the structured JSON object.
To obtain the source code, please use the GitHub Repository.
# Retrieve BRAVO Repository
git clone https://github.com/Fixel-Institute/BRAVO.git
cd BRAVO
# Get the most recent version
git checkout development
# Update Submodules
git submodule update --init --recursive
Dependencies
Software Packages
Python 3.70 or above
MySQL Databse
Node Package Manager 7 or above
React Frontend
React Frontend dependencies will be listed in package.json in Client folder for simplified installation.
Only the main packages will be shown below.
React (^18.2.0)
React Router DOM (^6.2.1)
Plotly.js (^2.14.0)
Axios (^0.27.2)
Material User Interface Design (^5.10.8)
Math.js (^11.2.1)
React Three Fiber (^8.8.8)
Python Server
Python Server dependencies will be listed in requirement.txt in Server folder for simplify installation.
Only the main packages will be shown below.
Django (Django==4.0.6)
Django Channels (channels==4.0.0)
Django REST Framework (djangorestframework==3.14.0)
MySQL Client (mysqlclient==2.1.1)
Daphne (daphne==3.0.2)
Matplotlib (matplotlib==3.5.2)
Cryptography (cryptography==37.0.4)
NiBabel (nibabel==4.0.2)
Numpy (numpy==1.23.1)
Scipy (scipy==1.9.0)
Scikit Learning (scikit_learn==1.1.3)
Spectrum (spectrum==0.8.1)
Pandas (pandas==1.4.3)
Date Utilities (python_dateutil==2.8.2 && pytz==2022.1)
HTTP Requests (requests==2.28.1)
Twilio SMS Service SDK (twilio==7.15.2)
Note
The packages listed above contain developmental features and may not be 100% neccessary for the basic usage. A trimmed version may be created in the future if some packages are not used anymore.
Docker Installation
Docker Images (Beta) are created for Client and Server component of the BRAVO Platform. Using Containerized Docker Images allow easier setup of BRAVO Platform in local computer for Windows and Mac. A Docker Compose file is created for people to pull/launch containeraized program via commandline easily. A guide of how to use Docker is shown in Docker Container Tutorials
React Frontend Installation Guide
The frontend webpage is written in React.js as a static standalone application. This means that the frontend webpage can be shared as a simple static folder without compilation. User may download pre-built application folder to host on their own server or use statically hosted webpage.
Build from Source (NPM)
For user who want to modify the frontend webpage and create their own routes, the source code is available on Github Repo. You will need to use NPM for installing dependencies and running build scripts.
The minimum node version required is v16. You may use Node Version Manager to download the desire node version.
Both NPM and NVM are easily accessible on Linux and MacOS. For Windows User, I recommend using Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) available on Windows 10 and Windows 11. You can build the source code like below:
# Change current working directory to BRAVO/Client
cd BRAVO/Client
# Install Dependencies with npm
npm install
# Hosting on 3000 port of your local computer
npm start
# Building static webpage for hosting
npm run build
If you are using the platform locally, you simply need to use npm start to start hosting the source code on your local computer.
This will also allow private network users accessing your webpage if they know your IP address and your 3000 port is open-accessed.
The built binaries will be available in the build folder in the Frontend source folder. You can upload all content of the folder to your desire hosting platform (locally with NGINX or Apache2, or online hosting platform like AWS S3 or Cloudflare Pages) if you want to make it statically available. However, putting them on public HTTPS page will require user to put their backend on either “localhost” or another publically available HTTPS endpoint for security issue.
If you desire to host your webpage on private HTTP, you should ensure your frontend is also hosted on private HTTP host as well.
If you do not wish to use Port 80 for http, you can simply use npm start to host your webpage and it will work just fine.
Python Server Installation Guide (Linux)
The procedure described here are tested on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS with source file directly clone through GitHub. The procedure here are describing for both HTTP deployment (internal use only) and HTTPS deployment (public release).
If you intend to deploy this software for public, I highly recommend using Linux deployment procedure for HTTPS. This tutorial will also cover for procedure to setup Amazon Web Service Elastic Cloud Compute (EC2) platform to work with Django Project.
Linux Step 0: Environment Setup
Install dependencies packages using apt-get is the simpliest way to start.
We will install MySQL and Python3 Virtual Environment to setup the conditions for server.
It is also noted that the default Python distribution on Ubuntu 18.04 is Python 3.6, therefore not satisfying the requirement.
You need to either manually update the Python distribution so that python3 --version is up-to-date or use Ubuntu 20.04 LTS,
which comes with Python 3.8.
All procedure assume that your working directory is the main directory of the cloned Git folder (i.e.: /home/ubuntu/BRAVO/Server).
# Set our current working directory as the SCRIPT_DIR
SCRIPT_DIR="$( cd -- "$( dirname -- "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" &> /dev/null && pwd )"
# Install Dependencies with Apt
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install python3-pip libjpeg-dev libjpeg8-dev libpng-dev nginx python3-virtualenv libmysqlclient-dev mysql-server docker.io cron
# Setup Redis Server on Docker for Django Channels
sudo docker run -p 6379:6379 -d redis:5
# Create Virutal Environment for Python called "venv"
virtualenv $SCRIPT_DIR/venv
source $SCRIPT_DIR/venv/bin/activate
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Linux Step 1: SQL Databse Setup
SQL Database will be used to store account information, patient entries, device entries, and various recording information. Due to the data size, neural recordings are not directly stored in database, but instead stored locally in binary format at the DataStorage folder. A data pointer that associate local files with patient recording will be stored in database for ease-of-access.
SQL Database will require manual creation prior to main server installation unless an existing database is used. You can access MySQL Database (the default database used for the installation script, but other database can be used.) through the following scripts.
sudo mysql -u root
# this would prompt you to enter admin password here for superuser privilege.
# Following commands are within mysql command-line-interface
# Create database named "BRAVOServer"
mysql> CREATE DATABASE BRAVOServer;
# Create a user that can access the database called "BRAVOAdmin" with an admin password called "AdminPassword"
# Change these values to what you see fit.
mysql> CREATE USER 'BRAVOAdmin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'AdminPassword';
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON BRAVOServer.* TO 'BRAVOAdmin'@'localhost';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
# exit MySQL Interface
mysql> exit
Once the account is set-up and database is created. You can edit the Server/mysql.config file to
reflect actual accses credential for your database.
Linux Step 2: Server Environment Variables
Environment variable for Python server is saved as a JSON file named .env. Python will load in the file content during load time.
An example environment file looks like the following.
{
"DATASERVER_PATH": "/home/ubuntu/DataStorage/",
"PYTHON_UTILITY": "/home/ubuntu/BRAVO/Server/modules/python-scripts",
"ENCRYPTION_KEY": "4LLHi6IJ0PRdneDJo48kCcBf3tHTLRXQ_tyKfttDIm0=",
"SERVER_ADDRESS": "bravo-server.jcagle.solutions",
"CLIENT_ADDRESS": "bravo-client.jcagle.solutions",
"MODE": "DEBUG"
}
DATASERVER_PATH
Absolute path to the folder storing all non-SQL data (TimeSeries and others).
You should have read/write or owner permission on the folder.
The folder should contain 3 subfolders for organization: cache, sessions, and recordings.
PYTHON_UTILITY
Absolute path to the folder containing Python Utility files. This is a submodule path in Server folder, and it is also where you can put your custom Python scripts.
ENCRYPTION_KEY
Fernet Cryptography, it is recommended to generate this string in Python using the following code.
from cryptography import fernet
fernet.Fernet.generate_key().decode("utf-8")
# Output: 'uCskkPv8pVyF9r0tSXQs2hvD7YYs-eS8nP7pkwz0vps='
SECRET_KEY
This is a web-server specific key for cryptographic signing for session cookies. DO NOT let others get your key, otherwise they can modify cookies sent by our server.
SERVER_ADDRESS and CLIENT_ADDRESS
The server address to access the Python Server. This can be the same as your React Frontend address (CLIENT_ADDRESS) if you setup Proxy for it. If not, configure both string to the correct path.
MODE
The Django operating mode. DEBUG allow more error log in case if an error is shown.
During development, you may keep it as DEBUG but set to PRODUCTION when done.
Linux Step 3: Django - MySQL Database Initialization
Initial migration is required to setup the Database to the required structure of Django Server.
This only need to be run once, unless a change is made to Server/Backend/models.py file.
python3 $SCRIPT_DIR/manage.py makemigrations Backend
python3 $SCRIPT_DIR/manage.py migrate
Linux Step 4: SSL (HTTPS) Certificate (Optional)
This step is not neccessary for local deployment. However, for people who want additional security to deploy with HTTPS, we will provide guidance for obtaining simple certificates for SSH.
The most common tool for free SSL certificate is through CertBot.
Refer to CertBot site to install tool on your server computer.
First, you can configure your DNS record to have your server address ($YOUR_SERVER_ADDRESS) point to your server IP.
Then run the following script to obtain your SSL certificate.
The output certificates should be saved in a directory at /etc/letsencrypt/live/$YOUR_SERVER_ADDRESS/.
sudo certbot certonly --standalone --preferred-challenges http -d $YOUR_SERVER_ADDRESS
A bare-minimum sample nginx configuration file deployment.conf is in Server directory as a reference to create a working reverse proxy server to direct SSL traffic to your server.
This configuration file should be saved in /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ directory and you should reload your nginx service whenever a change is made to the configuration.
Linux Step 5: Deployment
Due to the use of Websocket for real-time analysis, the default operating condition is through
Asynchronized Server Gateway Interface (ASGI) as opposed to the default Web Server Gateway Interface (WSGI) for Python.
To use ASGI, we use daphne to start our server. A standard startup script startServer.sh is available in Server folder for reference.
#/bin/bash
SCRIPT_DIR=$( cd -- "$( dirname -- "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" &> /dev/null && pwd )
# To start with WSGI - Django Channels Disabled
$SCRIPT_DIR/venv/bin/python3 $SCRIPT_DIR/manage.py runserver 0:3001
# To start with ASGI - Django Channels Enabled.
$SCRIPT_DIR/venv/bin/daphne -p 3001 -b 0.0.0.0 BRAVO.asgi:application
Warning
Due to how daphne is looking for Python modules, the working directory must be in “Server” folder for the command to work.
A more advanced SSL Certificate and Automatic Background Service tutorial can be found at Secure BRAVO Server with SSL Certificate tutorial page.
Linux Step 6: Processing Queue Service
In Version 2.2 and beyond, data processing is done through Processing Queue Service script. Once a while is uploaded, the file will be shown in Processing Queue.
To actually start the backend processing, user must execute the Processing Queue script.
# Working Directory is your BRAVO Folder, $SCRIPT_DIR
./Server/ProcessingQueueJob.sh
This script is recommended to be run with Cron in Linux for scheduled execution to reduce user interaction.
An example Crontab Script is available at Server/cron-job. Add these lines to your user’s crontab to allow the
processing queue to be run periodically.
Warning
It should be noted that if the BRAVO Server is started as a User service, the crontab has to be the user’s crontab (without sudo command).
sudo crontab -e is not the same as crontab -e.
Python Server Installation Guide (Windows)
The Windows Deployment for BRAVO 2.0 will be different from the original BRAVO_SSR Windows Deployment. The original BRAVO_SSR deplyoment for Windows focus on making Django working with Windows-specific MySQL Database and Apache Server. However, we decide to move toward making things easier by using the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL).
Using WSL, the deployment is essentially identical to Linux procedure with a few modifications. However, these procedure are not recommended for production purposes. I still recommend actual Linux Server as the production server host. However, Windows can still be used as developmental server to test capabilities.
Windows Step 0: Environment Setup
WSL can be enabled on Windows computer running Windows 10 Anniversary Update or newer builds. A good tutorial for WSL can be found at Microsoft Learning page.
In additional to WSL, we will also be using Visual Studio Code as our primary development environment. VS Code has a useful plugins that enable direct development in WSL. A tutorial on installing WSL plugins is available. With this plugin, you can run build scripts directly on WSL. For our tutorial, we will be installing WSL Version 2, to have maximum compatibility with Docker for Windows.
A third dependencies is Docker. docker.io package is available on WSL but Docker operates better with Desktop Application tunnel through WSL 2.
You may download Docker Desktop for Windows through their docker tutorial.
The rest of the installation procedure is assumed for you to be in WSL environment using VS Code integration with WSL.
Install dependencies packages using apt-get is the simpliest way to start.
We will install MySQL and Python3 Virtual Environment to setup the conditions for server.
It is also noted that the default Python distribution on Ubuntu 18.04 is Python 3.6, therefore not satisfying the requirement.
You need to either manually update the Python distribution so that python3 --version is up-to-date or use Ubuntu 20.04 LTS,
which comes with Python 3.8 or Ubuntu 22.04 LTS which comes with Python 3.10.
All procedure assume that your working directory is the main directory of the cloned Git folder (i.e.: /mnt/d/GitHub/BRAVO).
# Set our current working directory as the SCRIPT_DIR
SCRIPT_DIR="$( cd -- "$( dirname -- "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" &> /dev/null && pwd )"
# Install Dependencies with Apt
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install python3-pip libjpeg-dev libjpeg8-dev libpng-dev python3-virtualenv libmysqlclient-dev mysql-server
# Setup Redis Server on Docker for Django Channels
docker run -p 6379:6379 -d redis:5
# NOTE: You can also opt to install Redis via Docker Desktop GUI directly.
# Create Virutal Environment for Python called "venv"
virtualenv $SCRIPT_DIR/venv
source $SCRIPT_DIR/venv/bin/activate
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Windows Step 1: SQL Databse Setup
SQL Database will be used to store account information, patient entries, device entries, and various recording information. Due to the data size, neural recordings are not directly stored in database, but instead stored locally in binary format at the DataStorage folder. A data pointer that associate local files with patient recording will be stored in database for ease-of-access.
SQL Database will require manual creation prior to main server installation unless an existing database is used. You can access MySQL Database (the default database used for the installation script, but other database can be used.) through the following scripts.
It is also important to note that WSL does not have systemd for automatic background service startup.
To start MySQL server, you should call sudo service mysql start manually to activate mysql service.
# Start MySQL if not started yet
sudo service mysql start
# this would prompt you to enter admin password here for superuser privilege.
sudo mysql -u root
# Following commands are within mysql command-line-interface
# Create database named "BRAVOServer"
mysql> CREATE DATABASE BRAVOServer;
# Create a user that can access the database called "BRAVOAdmin" with an admin password called "AdminPassword"
# Change these values to what you see fit.
mysql> CREATE USER 'BRAVOAdmin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'AdminPassword';
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON BRAVOServer.* TO 'BRAVOAdmin'@'localhost';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
# exit MySQL Interface
mysql> exit
Once the account is set-up and database is created. You can edit the Server/mysql.config file to
reflect actual accses credential for your database.
Note
Given how WSL handles permission. If your folder is cloned on your /mnt drive, you must modify the file’s permission on Windows end to allow it
to be read by Django. After you finish editing the config file, you must disable inheritance of permission from parent object. Then you remove all user
permission, leave only Authenticated User group with Read and Read/Execute Access only (not even write access). This will avoid
[World Writable] permission error.
Windows Step 2: Server Environment Variables
Environment variable for Python server is saved as a JSON file named .env. Python will load in the file content during load time.
An example environment file looks like the following.
{
"DATASERVER_PATH": "/home/ubuntu/DataStorage/",
"PYTHON_UTILITY": "/home/ubuntu/BRAVO/Server/modules/python-scripts",
"ENCRYPTION_KEY": "uCskkPv8pVyF9r0tSXQs2hvD7YYs-eS8nP7pkwz0vps=",
"SECRET_KEY": "django-insecure-v#a8t(pk6jhgdkujyrkuoiyrfkuyk4&)+jjkhfg(!ea+",
"SERVER_ADDRESS": "bravo-server.jcagle.solutions",
"CLIENT_ADDRESS": "https://bravo-client.jcagle.solutions",
"MODE": "DEBUG"
}
DATASERVER_PATH
Absolute path to the folder storing all non-SQL data (TimeSeries and others).
You should have read/write or owner permission on the folder.
The folder should contain 3 subfolders for organization: cache, sessions, and recordings.
PYTHON_UTILITY
Absolute path to the folder containing Python Utility files. This is a submodule path in Server folder, and it is also where you can put your custom Python scripts.
ENCRYPTION_KEY
Fernet Cryptography key, it is recommended to generate this string in Python using the following code.
from cryptography import fernet
fernet.Fernet.generate_key().decode("utf-8")
# Output: 'uCskkPv8pVyF9r0tSXQs2hvD7YYs-eS8nP7pkwz0vps='
SECRET_KEY
This is a web-server specific key for cryptographic signing for session cookies. DO NOT let others get your key, otherwise they can modify cookies sent by our server.
SERVER_ADDRESS and CLIENT_ADDRESS
The server address to access the Python Server. This can be the same as your React Frontend address (CLIENT_ADDRESS) if you setup Proxy for it. If not, configure both string to the correct path. The client address must include HTTP or HTTPS prefix.
MODE
The Django operating mode. DEBUG allow more error log in case if an error is shown.
During development, you may keep it as DEBUG but set to PRODUCTION when done.
Windows Step 3: Django - MySQL Database Initialization
Initial migration is required to setup the Database to the required structure of Django Server.
This only need to be run once, unless a change is made to Server/Backend/models.py file.
Note
It is still not clear to me why WSL require us to have sudo privilege to access mysql socket. However,
if you do not have superuser privilege, you may encounter ERROR 2002 (HY000): Can't connect to local MySQL server through socket '/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock' (2)
error even though you can verify that MySQL is up and running.
sudo $SCRIPT_DIR/venv/bin/python3 $SCRIPT_DIR/manage.py makemigrations Backend
sudo $SCRIPT_DIR/venv/bin/python3 $SCRIPT_DIR/manage.py migrate
Windows Step 4: Deployment
Deployment in Windows can be done primarily through VS Code integrated with WSL. Once you open BRAVO Folder through WSL, you may observe the following indication that you are in WSL environment.

We have created a sample .vscode/tasks.json file that describe standard deployment scripts for you.
Go to Terminal -> Run Task in VS Code and you will see BRAVO Server deployment configuration. Running it will
bring up WSL Terminal, which will run the following pipeline to start BRAVO Server. You may modify paths and variables in .vscode/tasks.json
for your needs.
cd ${cwd}/Server;
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql start;
sudo ${cwd}/Server/venv/bin/daphne -p 3001 -b 0.0.0.0 BRAVO.asgi:application
Windows Step 5: Processing Queue Service
In Version 2.2 and beyond, data processing is done through Processing Queue Service script. Once a while is uploaded, the file will be shown in Processing Queue.
To actually start the backend processing, user must execute the Processing Queue script.
# Working Directory is your BRAVO Folder, $SCRIPT_DIR
./Server/ProcessingQueueJob.sh
Python Server Installation Guide (MacOS)
Installation of Python Server on MacOS follows the same process as Linux operating system. However,
due to the lack of apt-get, MacOS user must download neccessary dependencies manually.
MacOS Step 0: Environment Setup
We will need to install MySQL, Docker with Redis, and Python3 Virtual Environment to setup the conditions for server. If you do not have Python3 on your Mac, you should download that via official Python Page.
You can setup MySQL on Mac using MySQL Community Server. Once downloaded and installed,
check System Preferences on MacOS and you should see a new option is now available at the bottom of the page, called “MySQL”.
Click on MySQL to ensure that it is currently active. You can turn off/on the server manually or to set MySQL to start when computer startup.
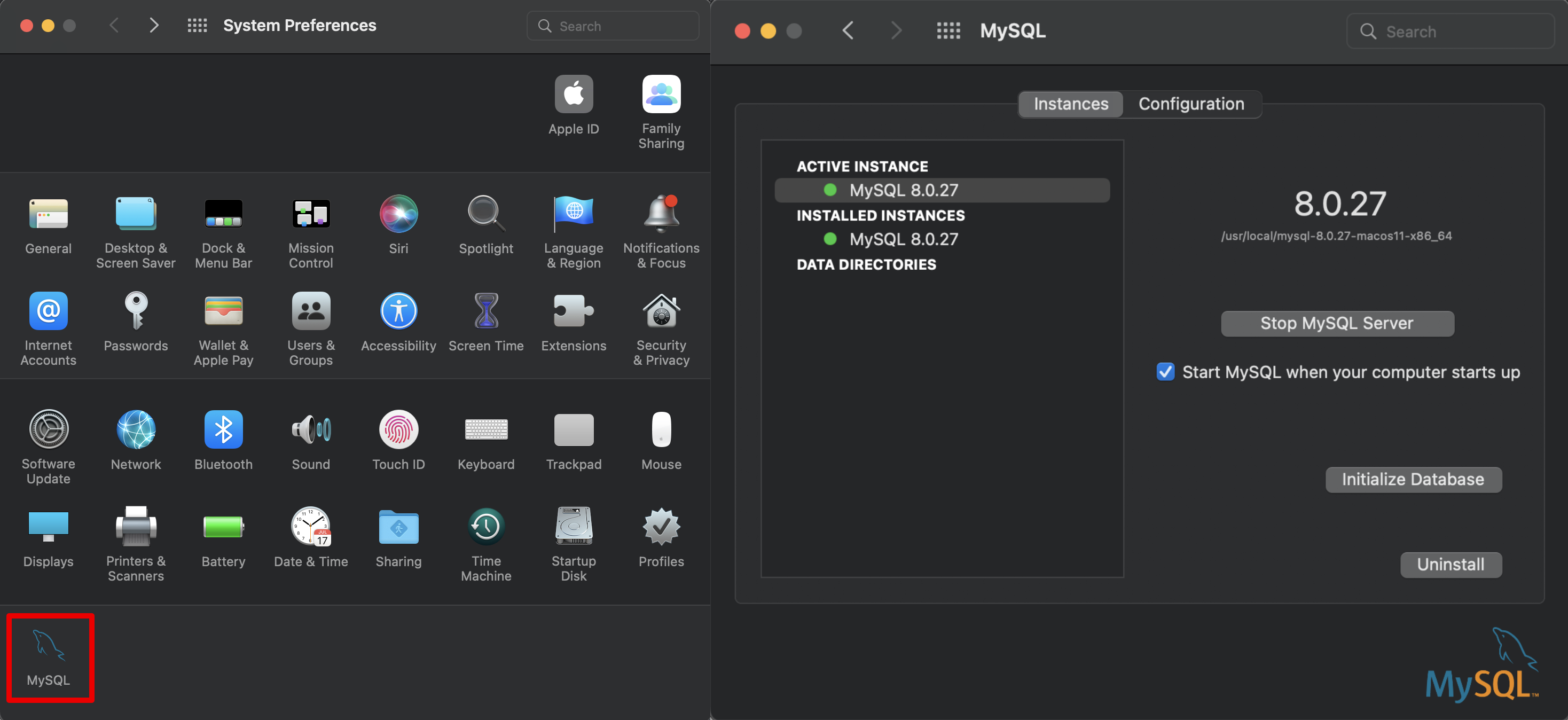
You will also need docker and redis for Django Channels.
You can install docker for MacOS using Docker Desktop.
Once installed, you can open Docker in your Application folder and confirm it is running.
To install Redis, you can call docker pull redis in MacOS Terminal.
Confirm redis is installed by checking “Images” in Docker Desktop.
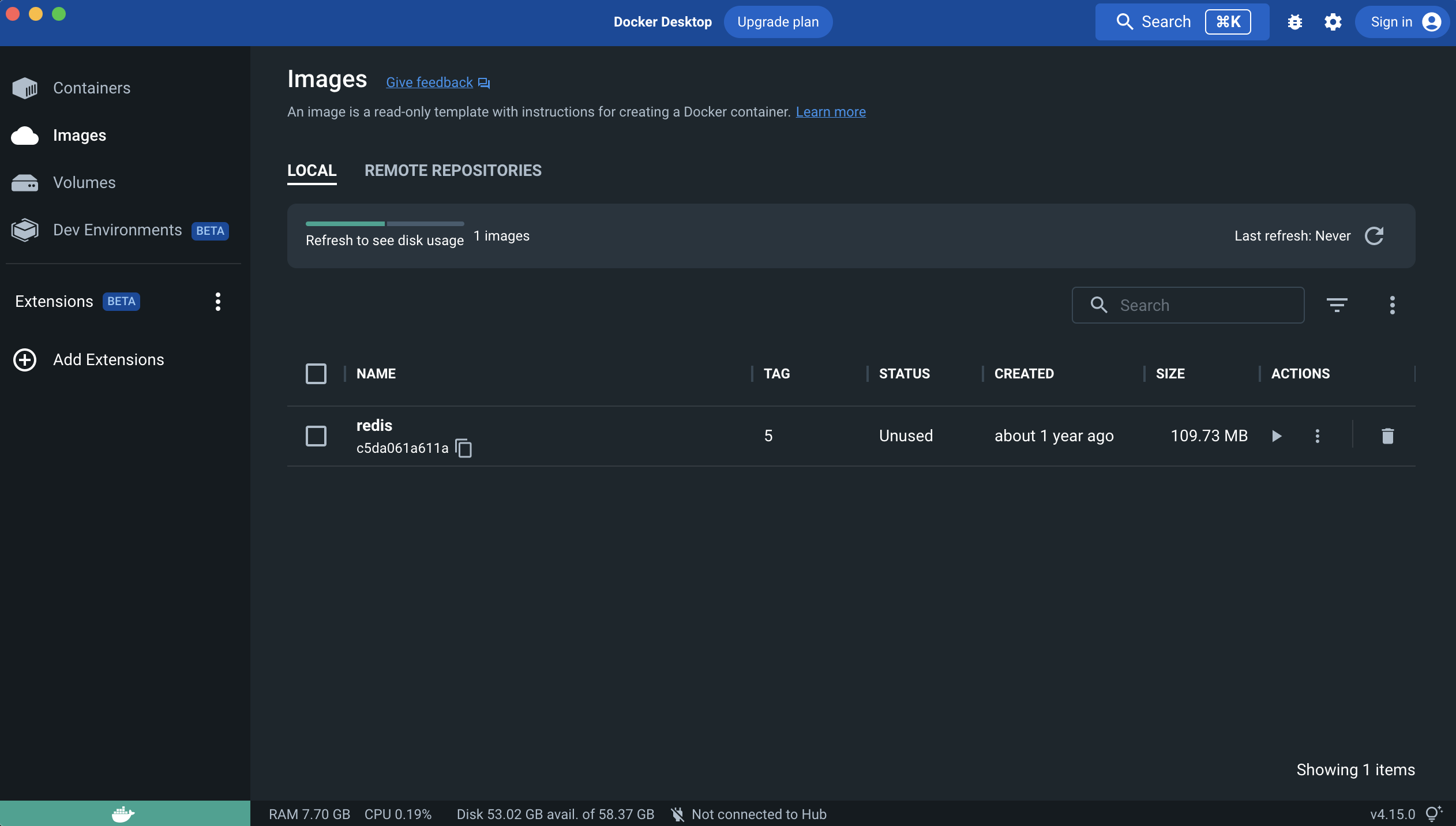
You now have all the software requirement (except Apache/NGINX, which will not be covered here because I do not recommend using MacOS for hosting public application). The following script go over the rest of the dependencies installation for Python3 using Virtual Environment.
All procedure assume that your working directory is the main directory of the cloned Git folder
(i.e.: /Users/Username/Documents/Github/BRAVO/Server).
# Set our current working directory as the SCRIPT_DIR
SCRIPT_DIR="$( cd -- "$( dirname -- "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" &> /dev/null && pwd )"
# Setup Redis Server on Docker for Django Channels
docker run -p 6379:6379 -d redis:5
# Create Virutal Environment for Python called "venv"
virtualenv $SCRIPT_DIR/venv
source $SCRIPT_DIR/venv/bin/activate
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
MacOS Step 1: SQL Databse Setup
SQL Database will be used to store account information, patient entries, device entries, and various recording information. Due to the data size, neural recordings are not directly stored in database, but instead stored locally in binary format at the DataStorage folder. A data pointer that associate local files with patient recording will be stored in database for ease-of-access.
SQL Database will require manual creation prior to main server installation unless an existing database is used. You can access MySQL Database (the default database used for the installation script, but other database can be used.)
sudo mysql -u root
# this would prompt you to enter admin password here for superuser privilege.
# Following commands are within mysql command-line-interface
# Create database named "BRAVOServer"
mysql> CREATE DATABASE BRAVOServer;
# Create a user that can access the database called "BRAVOAdmin" with an admin password called "AdminPassword"
# Change these values to what you see fit.
mysql> CREATE USER 'BRAVOAdmin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'AdminPassword';
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON BRAVOServer.* TO 'BRAVOAdmin'@'localhost';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
# exit MySQL Interface
mysql> exit
Once the account is set-up and database is created. You can edit the Server/mysql.config file to
reflect actual accses credential for your database.
MacOS Step 2: Server Environment Variables
Environment variable for Python server is saved as a JSON file named .env. Python will load in the file content during load time.
An example environment file looks like the following.
{
"DATASERVER_PATH": "/home/ubuntu/DataStorage/",
"PYTHON_UTILITY": "/home/ubuntu/BRAVO/Server/modules/python-scripts",
"ENCRYPTION_KEY": "uCskkPv8pVyF9r0tSXQs2hvD7YYs-eS8nP7pkwz0vps=",
"SECRET_KEY": "django-insecure-v#a8t(pk6jhgdkujyrkuoiyrfkuyk4&)+jjkhfg(!ea+",
"SERVER_ADDRESS": "bravo-server.jcagle.solutions",
"CLIENT_ADDRESS": "https://bravo-client.jcagle.solutions",
"MODE": "DEBUG"
}
DATASERVER_PATH
Absolute path to the folder storing all non-SQL data (TimeSeries and others).
You should have read/write or owner permission on the folder.
The folder should contain 3 subfolders for organization: cache, sessions, and recordings.
PYTHON_UTILITY
Absolute path to the folder containing Python Utility files. This is a submodule path in Server folder, and it is also where you can put your custom Python scripts.
ENCRYPTION_KEY
Fernet Cryptography key, it is recommended to generate this string in Python using the following code.
from cryptography import fernet
fernet.Fernet.generate_key().decode("utf-8")
# Output: 'uCskkPv8pVyF9r0tSXQs2hvD7YYs-eS8nP7pkwz0vps='
SECRET_KEY
This is a web-server specific key for cryptographic signing for session cookies. DO NOT let others get your key, otherwise they can modify cookies sent by our server.
SERVER_ADDRESS and CLIENT_ADDRESS
The server address to access the Python Server. This can be the same as your React Frontend address (CLIENT_ADDRESS) if you setup Proxy for it. If not, configure both string to the correct path. The client address must include HTTP or HTTPS prefix.
MODE
The Django operating mode. DEBUG allow more error log in case if an error is shown.
During development, you may keep it as DEBUG but set to PRODUCTION when done.
MacOS Step 3: Django - MySQL Database Initialization
Initial migration is required to setup the Database to the required structure of Django Server.
This only need to be run once, unless a change is made to Server/Backend/models.py file.
python3 $SCRIPT_DIR/manage.py makemigrations Backend
python3 $SCRIPT_DIR/manage.py migrate
Warning
The new BRAVO Server Database has significant difference when compared to the original BRAVO platform v0.1 released in 2021. The database are not convertable at the moment, but a migration script is in development to help as much migration as possible.
MacOS Step 4: Deployment
Due to the use of Websocket for real-time analysis, the default operating condition is through
Asynchronized Server Gateway Interface (ASGI) as opposed to the default Web Server Gateway Interface (WSGI) for Python.
To use ASGI, we use daphne to start our server. A standard startup script startServer.sh is available in Server folder for reference.
#/bin/bash
SCRIPT_DIR=$( cd -- "$( dirname -- "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" &> /dev/null && pwd )
# To start with WSGI - Django Channels Disabled
#$SCRIPT_DIR/venv/bin/python3 $SCRIPT_DIR/manage.py runserver 0:3001
# To start with ASGI - Django Channels Enabled.
$SCRIPT_DIR/venv/bin/daphne -p 3001 -b 0.0.0.0 BRAVO.asgi:application
Warning
Due to how daphne is looking for Python modules, the working directory must be in “Server” folder for the command to work.
Danger
If you encounter an error that shows NameError: name '_mysql' is not defined. You are using a MacOS version that
doesn’t handle MySQL Client properly. The easiest solution is a post provided by Adan Johnson on
How to use PyMySQL with Django.
To summarize, you should install PyMySQL pip3 install PyMySQL and edit Server/BRAVO/setting.py in the following manner.
# Find this code block
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'OPTIONS': {
'read_default_file': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'mysql.config'),
'init_command': "SET sql_mode='STRICT_TRANS_TABLES'"
},
}
}
# Add the following 3 lines right below it
import pymysql
pymysql.version_info = (1, 4, 2, "final", 0)
pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()
MacOS Step 5: Processing Queue Service
In Version 2.2 and beyond, data processing is done through Processing Queue Service script. Once a while is uploaded, the file will be shown in Processing Queue.
To actually start the backend processing, user must execute the Processing Queue script.
# Working Directory is your BRAVO Folder, $SCRIPT_DIR
./Server/ProcessingQueueJob.sh
This script is recommended to be run with Cron in Linux for scheduled execution to reduce user interaction.
An example Crontab Script is available at Server/cron-job. Add these lines to your user’s crontab to allow the
processing queue to be run periodically.
Warning
It should be noted that if the BRAVO Server is started as a User service, the crontab has to be the user’s crontab (without sudo command).
sudo crontab -e is not the same as crontab -e.